Focos
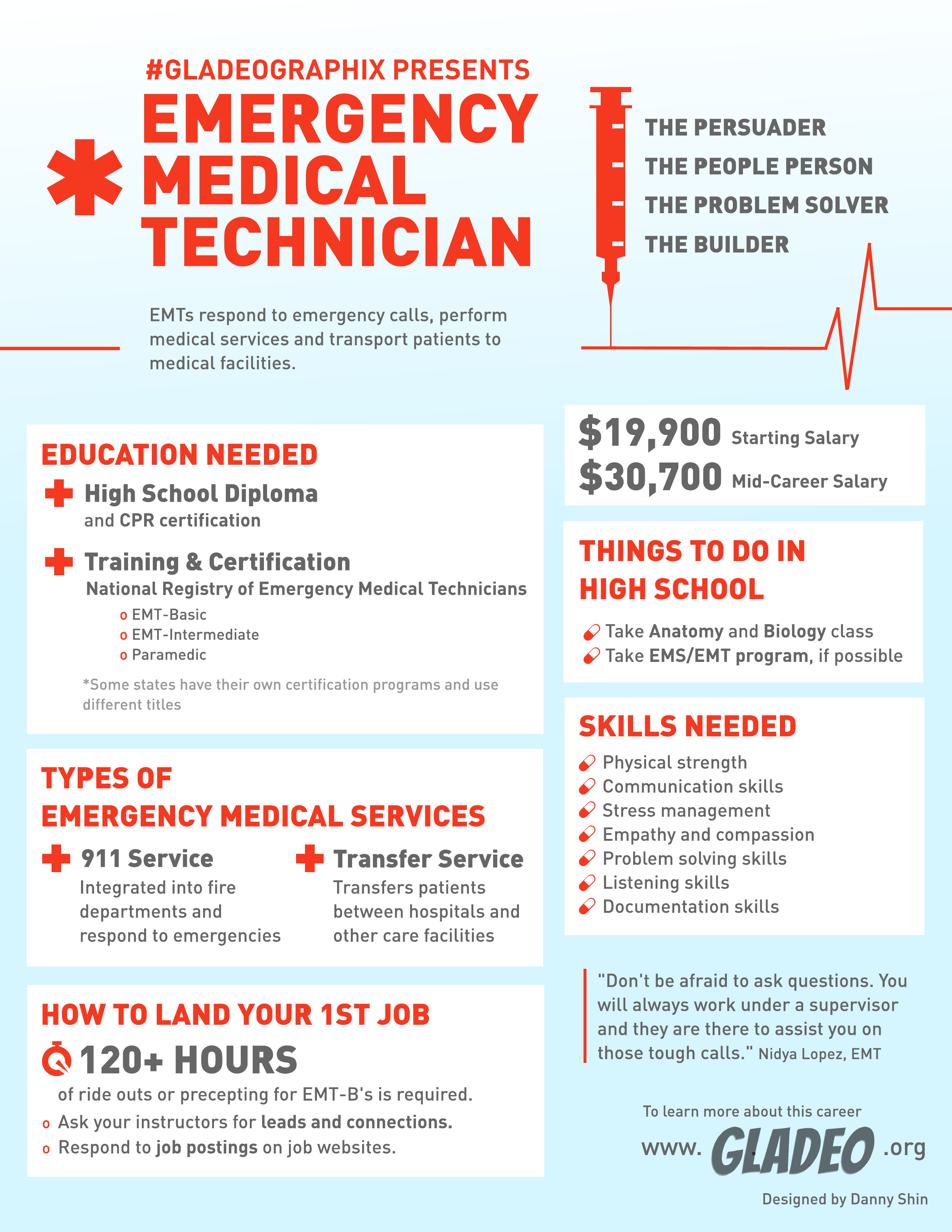
First Responder, EMT, EMT – Basic, EMT – Intermediate, Paramedic, Flight Paramedic
EMTs respond to emergency calls, perform medical services and transport patients to medical facilities.
- Helping people every day!
- Everyday is a different day.
- The rush!
“Helping others! The best is when you actually see the thankful people later. Sometimes I’d bump into people I’ve cared for at the store or something. I had a lady hug me once and told me I was an angel because I picked her husband up several times when he was having withdrawals. Getting cardiac arrest patients back feels awesome…Breaking down doors or windows to get to patients is always cool.” Nidya Lopez, EMT
Note: Varies between stations.
- 0600: Shift change. Receive outgoing report. Clean/Check equipment. Check supply and medicine inventory.
- 0600-0700: Clean station
- 0700-0800: Breakfast
- 0800-1200: Training/Personal time
- 1200-1300: Lunch
- 1300-1800: Training/Personal Time/Work out
- 1800-1900: Dinner
- 1900-0545: Personal time/Sleep
- 0545: Wake up tones
Calls
The above schedule obviously does not include the average 10-20 calls per day that are split between the fire stations in the area. The time spent on a call can vary from 30 minutes to several hours or more and may involve one or two engines or every piece of available apparatus. This can have a significant impact on the schedule for the day and many times training or maintenance must be rescheduled to another day.
- Responds to 911 calls for emergency medical assistance, such as cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) or bandaging a wound.
- Assesses a patient’s condition and determines a course of treatment.
- Follows guidelines that they learned in training and that they receive from physicians who oversee their work.
- Uses backboards and restraints to keep patients still and safe in an ambulance for transport.
- Help stransfer patients to the emergency department of a healthcare facility and reports their observations and treatment to the staff.
- Creates a patient care report; documenting the medical care they gave the patient.
- Replaces used supplies and check or clean equipment after use.
- Physical strength: Must be able to lift heavy objects.
- Communication skills: Must be able to clearly articulate patient’s condition to healthcare provider to which you are transferring patient.
- Stress management: Must be able to deal with stress and extreme environments.
- Empathy and compassion: Must be able to provide emotional support patients in an emergency.
- Problem-solving skills under stressful situations
- Listening skills: Must listen well to the patients to determine the injury or illness.
- Documentation skills: accuracy and thorough recordings of situation, injury or illness.
1. 911 services: Integrated into fire departments and respond to emergencies.
2. Transfer services: Transfers patients between hospitals and other care facilities.
Modes of transport: ambulance, rescue vehicle, helicopter, fixed-wing aircraft, motorcycle, or fire suppression apparatus (aka fire truck).
- You are on the front line: You are pre-hospital care so you will see all types situations (trauma, gunshot victim, gruesome accidents...etc.).
- Dangerous and life-threatening.
- Irregular and long hours when on call.
- Liked the outdoors.
- Liked helping people in need.
- Attracted to adrenaline-filled activities.
- At a minimum, Emergency Medical Technicians (EMTs) must complete a non-degree EMT program, which can be completed at either a community college or vocational training institute
- These programs usually require prior completion of the American Heart Association’s Basic Life Support CPR course
- Programs should be accredited by the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs. Hybrid programs feature online components
- EMT training can run from only three months up to a year
- En National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians (NREMT) lists the following training levels:
- Emergency Medical Responder
- Emergency Medical Technician
- Advanced Emergency Medical Technician (requires an extra 400 hours of training)
- Paramedic (requires an extra ~1,200 hours of training and at least an associate’s)
- EMTs must pass the NREMT’s national exam and obtain state licensure to work. Some states may have additional requirements, including passing a background check
- In high school, stock up on classes such as anatomy and physiology
- Sign up for an EMT training program that works for your schedule. The more hands-on training you can get, the better, but plenty of the subject matter can be effectively learned remotely
- Remember, you aren’t just learning to pass tests but to help save lives in real-world situations
- Knock out your American Heart Association’s Basic Life Support CPR course and make sure it is still valid when applying for jobs. Certification is good for two years, then a renewal class must be taken
- EMT field internships may be a way for qualified students to gain experience
- Engage in routine physical exercise to build the strength and stamina needed for long shifts
- EMTs treat a wide range of patients under stressful circumstances. Become familiar with other cultures so you can ensure good communications
- In particular, knowing Spanish can give you an advantage in many employment situations
- Learn tips for staying calm under pressure and for helping patients stay calm, too
- 17% with HSDiploma
- 20% with Associate’s
- 12.7% with Bachelor’s
- 1.6% with Master’s
- 1.1% with Doctoral
- If possible, apply for Emergency Medical Technicians internships while still a student! Most departments will have on the job type training b/c you are required 120+ hours of ride outs or precepting (instruction) for EMT-B’s. It’s a testing phase to see where you are in skills and patient care. Work hard and make relationships when you are training at these hospitals.
- Work hard and learn as much as you can during your intern experience. Ask your direct supervisor if they can serve as a reference when you go to apply for jobs
- Be proficient in using all EMT-related airway equipment, trauma supplies, medical devices, IVs, syringes, splints, disinfectants, and personal protective equipment
- Look for jobs and internships on Indeed, Simply Hired, Glassdoor, or other job portals
- Ask teachers for tips on job seeking! If your school has a career center, get help with your EMT resume and practice mock interviewing skills
- Review sample EMT interview questions to prepare ahead of time
- Always dress for interview success!
Having additional certifications like ACLS, ITLS, PALSAMLS, PHTLS, PEEP, BTLS make your resume more appealing. Most of those are required for paramedics and are provided by the organization after hire.
Páginas web
- American Academy of Emergency Medicine
- American Heart Association
- Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs
- EMS World
- Journal of Emergency Medical Services
- National Association of Emergency Medical Technicians
- National Fire Protection Association
- National Registry of Emergency Medical Technicians
- State EMS Agencies
Libros
- EMS Field Guide BLS Version: Revised 2021, by Jon Tardiff
- Medical Terminology: The Best and Most Effective Way to Memorize, Pronounce and Understand Medical Terms, by David Andersson, M. Mastenbjörk M.D., et al.
- NREMT Study Guide 2022-2023, by Newstone EMT
Alternate careers: Registered Nurse (very common), Firefighter
“Don’t be afraid to ask questions. You will always work under a supervisor and they are there to assist you on those tough calls.” Nidya Lopez, EMT
Noticias
Ofertas de empleo

Cursos y herramientas en línea